Advanced techniques such as null, FIN, Xmas, and idle (zombie) scans, spoofing, in addition to FW and IDS evasion.
https://tryhackme.com/room/nmap03
Task 1 - Introduction
We will cover the following types of port scans:
- Null Scan
- FIN Scan
- Xmas Scan
- Maimon Scan
- ACK Scan
- Window Scan
- Custom Scan
Moreover, we will cover the following:
- Spoofing IP
- Spoofing MAC
- Decoy Scan
- Fragmented Packets
- Idle/Zombie Scan
Task 2 TCP Null Scan, FIN Scan, and Xmas Scan
-sNNull scan - The null scan does not set any flag; all six flag bits are set to zero.-sFFIN scan - The FIN scan sends a TCP packet with the FIN flag set.-sXXmas scan - An Xmas scan sets the FIN, PSH, and URG flags simultaneously.
On scenario where these three scan types can be efficient is when scanning a target behind a stateless (non-stateful) firewall. A stateless firewall will check if the incoming packet has the SYN flag set to detect a connection attempt. Using a flag combination that does not match the SYN packet makes it possible to deceive the firewall and reach the system behind it. However, a stateful firewall will Boxly block all such crafted packets and render this kind of scan useless.
Answer the questions below
In a null scan, how many flags are set to 1? 0
In a FIN scan, how many flags are set to 1? 1
In a Xmas scan, how many flags are set to 1? 3
Start the VM and load the AttackBox. Once both are ready, open the terminal on the AttackBox and use nmap to launch a FIN scan against the target VM. How many ports appear as open/filtered? 7
| **Repeat your scan launching a null scan against the target VM. How many ports appear as open | filtered?** 7 |
Task 3 - TCP Maimon Scan
-sMIn this scan, the FIN and ACK bits are set. The target should send an RST packet as a response. This scan won’t work on most targets encountered in modern networks.
Answer the questions below
In the Maimon scan, how many flags are set? 2
Task 4 - TCP ACK, Window, and Custom Scan
-sATCP ACK scan. As the name implies, an ACK scan will send a TCP packet with the ACK flag set. This scan won’t tell us whether the target port is open in a simple setup. This kind of scan would be helpful if there is a firewall in front of the target.-sWTCP Window scan. On specific systems, this can reveal that the port is open. Similarly, launching a TCP window scan against a Linux system with no firewall will not provide much information. However, as you would expect, if we repeat our TCP window scan against a server behind a firewall, we expect to get more satisfying results.-scanflags CUSTOM_FLAGSif you want to set SYN, RST, and FIN simultaneously, you can do so.
It is essential to note that the ACK scan and the window scan were very efficient at helping us map out the firewall rules. However, it is vital to remember that just because a firewall is not blocking a specific port, it does not necessarily mean that a service is listening on that port. For example, there is a possibility that the firewall rules need to be updated to reflect recent service changes. Hence, ACK and window scans are exposing the firewall rules, not the services.
Answer the questions below
In TCP Window scan, how many flags are set? 1
You decided to experiment with a custom TCP scan that has the reset flag set. What would you add after --scanflags? RST
The VM received an update to its firewall ruleset. A new port is now allowed by the firewall. After you make sure that you have terminated the VM from Task 2, start the VM for this task. Launch the AttackBox if you haven’t done that already. Once both are ready, open the terminal on the AttackBox and use Nmap to launch an ACK scan against the target VM. How many ports appear unfiltered? 4
What is the new port number that appeared? 443
Is there any service behind the newly discovered port number? (Y/N) No
Task 5 - Spoofing and Decoys
nmap -e NET_INTERFACE -Pn -S SPOOFED_IP 10.10.141.22We can scan target systems with spoofed IP addresses and MAC addresses. For this scan to work and give accurate results, the attacker needs to monitor the network traffic to analyze the replies. Specify the network interface using-eand to explicitly disable ping scan-Pn.
When you are on the same subnet as the target machine, you would be able to spoof your MAC address as well. You can specify the source MAC address using –spoof-mac SPOOFED_MAC. This address spoofing is only possible if the attacker and the target machine are on the same Ethernet (802.3) network or same WiFi (802.11).
You can launch a decoy scan by specifying a specific or random IP address -D example: nmap -D 10.10.0.1,10.10.0.2,RND,RND,ME 10.10.141.22
Answer the questions below
What do you need to add to the command sudo nmap 10.10.141.22 to make the scan appear as if coming from the source IP address 10.10.10.11 instead of your IP address? -S 10.10.10.11
What do you need to add to the command sudo nmap 10.10.141.22 to make the scan appear as if coming from the source IP addresses 10.10.20.21 and 10.10.20.28 in addition to your IP address? -D 10.10.20.21,10.10.20.28,ME
Task 6 - Fragmented Packets
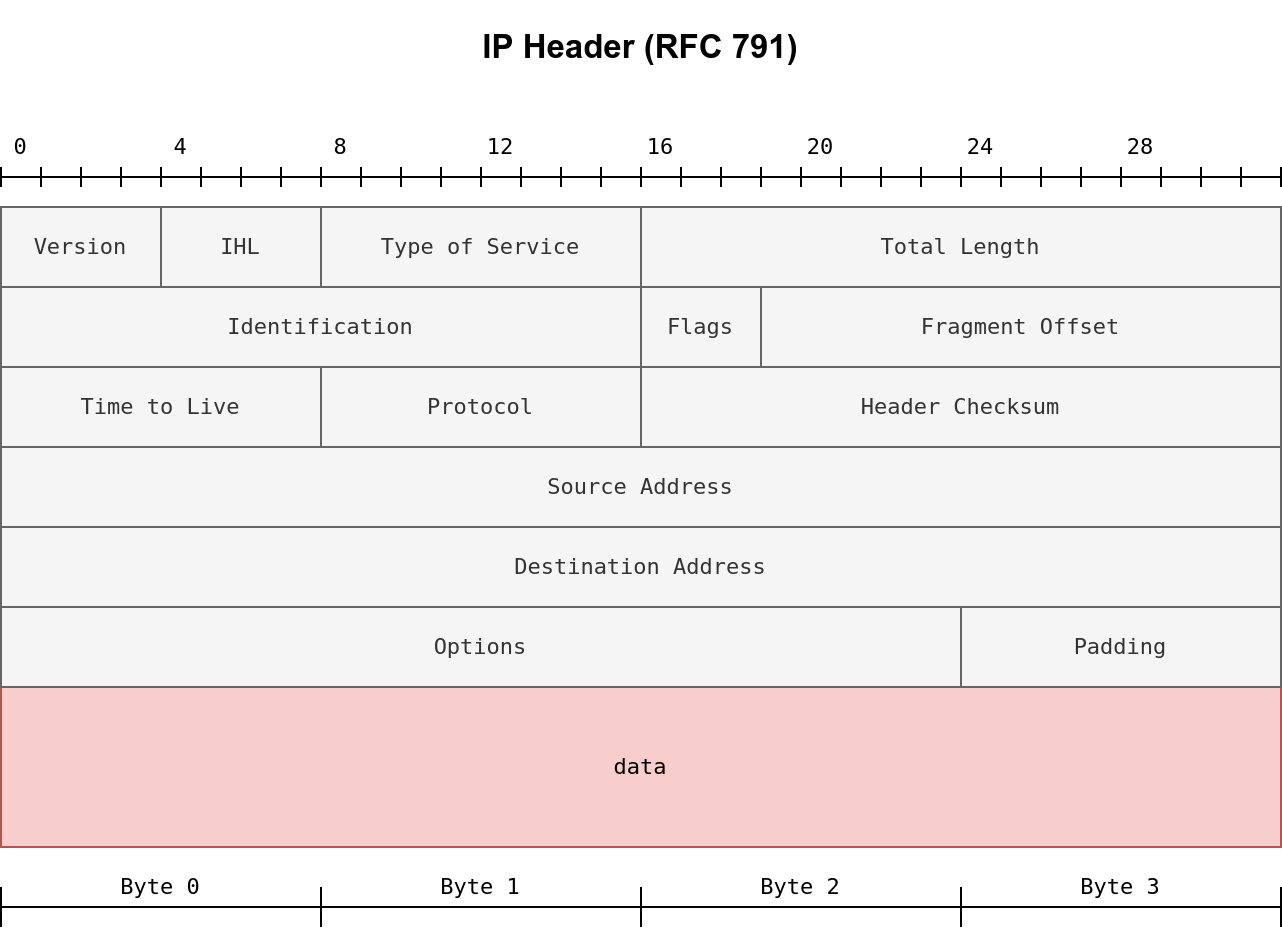
Nmap provides the option -f to fragment packets. Once chosen, the IP data will be divided into 8 bytes or less. Adding another -f (-f -f or -ff) will split the data into 16 byte-fragments instead of 8.
To properly understand fragmentation, we need to look at the IP header in the figure below.
Answer the questions below
If the TCP segment has a size of 64, and -ff option is being used, how many IP fragments will you get? If you added -ff (or -f -f), the fragmentation of the data will be multiples of 16.
Task 7 - Idle/Zombie Scan
nmap -sI ZOMBIE_IP 10.10.141.22, where ZOMBIE_IP is the IP address of the idle host (zombie).
The idle (zombie) scan requires the following three steps to discover whether a port is open:
- Trigger the idle host to respond so that you can record the current IP ID on the idle host.
- Send a SYN packet to a TCP port on the target. The packet should be spoofed to appear as if it was coming from the idle host (zombie) IP address.
- Trigger the idle machine again to respond so that you can compare the new IP ID with the one received earlier.
Answer the questions below
You discovered a rarely-used network printer with the IP address 10.10.5.5, and you decide to use it as a zombie in your idle scan. What argument should you add to your Nmap command? -sI 10.10.5.5
Task 8 - Getting More Details
--reason if you want Nmap to provide more details regarding its reasoning and conclusions. This flag gives us the explicit reason why Nmap concluded that the system is up or a particular port is open. For more detailed output, you can consider using -v for verbose output or -vv for even more verbosity.
If -vv does not satisfy your curiosity, you can use -d for debugging details or -dd for even more details. You can guarantee that using -d will create an output that extends beyond a single screen.
Answer the questions below
Launch the AttackBox if you haven’t done so already. After you make sure that you have terminated the VM from Task 4, start the VM for this task. Wait for it to load completely, then open the terminal on the AttackBox and use Nmap with nmap -sS -F –reason 10.10.237.236 to scan the VM. What is the reason provided for the stated port(s) being open? SYN-ACK
Task 9 - Summary
This room covered the following types of scans.
| Port Scan Type | Example Command |
|---|---|
| TCP Null Scan | sudo nmap -sN 10.10.203.92 |
| TCP FIN Scan | sudo nmap -sF 10.10.203.92 |
| TCP Xmas Scan | sudo nmap -sX 10.10.203.92 |
| TCP Maimon Scan | sudo nmap -sM 10.10.203.92 |
| TCP ACK Scan | sudo nmap -sA 10.10.203.92 |
| TCP Window Scan | sudo nmap -sW 10.10.203.92 |
| Custom TCP Scan | sudo nmap --scanflags URGACKPSHRSTSYNFIN 10.10.203.92 |
| Spoofed Source IP | sudo nmap -S SPOOFED_IP 10.10.203.92 |
| Spoofed MAC Address | --spoof-mac SPOOFED_MAC |
| Decoy Scan | nmap -D DECOY_IP,ME 10.10.203.92 |
| Idle (Zombie) Scan | sudo nmap -sI ZOMBIE_IP 10.10.203.92 |
| Fragment IP data into 8 bytes | -f |
| Fragment IP data into 16 bytes | -ff |
| Option | Purpose |
|---|---|
--source-port PORT_NUM | specify source port number |
--data-length NUM | append random data to reach given length |
These scan types rely on setting TCP flags in unexpected ways to prompt ports for a reply. Null, FIN, and Xmas scan provoke a response from closed ports, while Maimon, ACK, and Window scans provoke a response from open and closed ports.
| Option | Purpose |
|---|---|
--reason | explains how Nmap made its conclusion |
-v | verbose |
-vv | very verbose |
-d | debugging |
-dd | more details for debugging |