Learn in-depth how nmap TCP connect scan, TCP SYN port scan, and UDP port scan work.
https://tryhackme.com/room/nmap02
Task 1 - Introduction
This room and the next one, we focus on port scanning and the different types of port scans used by nmap. This room explains:
- TCP connect port scan
- TCP SYN port scan
- UDP port scan
Moreover, we discuss the different options to specify the ports, the scan rate, and the number of parallel probes.
Task 2 - TCP and UDP Ports
Oversimplified, we can classify ports in two states:
- Open port indicates that there is some service listening on that port.
- Closed port indicates that there is no service listening on that port.
In Box situations, we need to consider the impact of firewalls. For instance, a port might be open, but a firewall might be blocking the packets. Therefore, Nmap considers the following six states:
- Open: indicates that a service is listening on the specified port.
- Closed: indicates that no service is listening on the specified port, although the port is accessible. By accessible, we mean that it is reachable and is not blocked by a firewall or other security appliances/programs.
- Filtered: means that Nmap cannot determine if the port is open or closed because the port is not accessible. This state is usually due to a firewall preventing Nmap from reaching that port. Nmap’s packets may be blocked from reaching the port; alternatively, the responses are blocked from reaching Nmap’s host.
- Unfiltered: means that Nmap cannot determine if the port is open or closed, although the port is accessible. This state is encountered when using an ACK scan
-sA. Open Filtered: This means that Nmap cannot determine whether the port is open or filtered. Closed Filtered: This means that Nmap cannot decide whether a port is closed or filtered.
Answer the questions below
Which service uses UDP port 53 by default? DNS
Which service uses TCP port 22 by default? SSH
How many port states does Nmap consider? 6
Which port state is the most interesting to discover as a pentester? OPEN!
Task 3 - TCP Flags
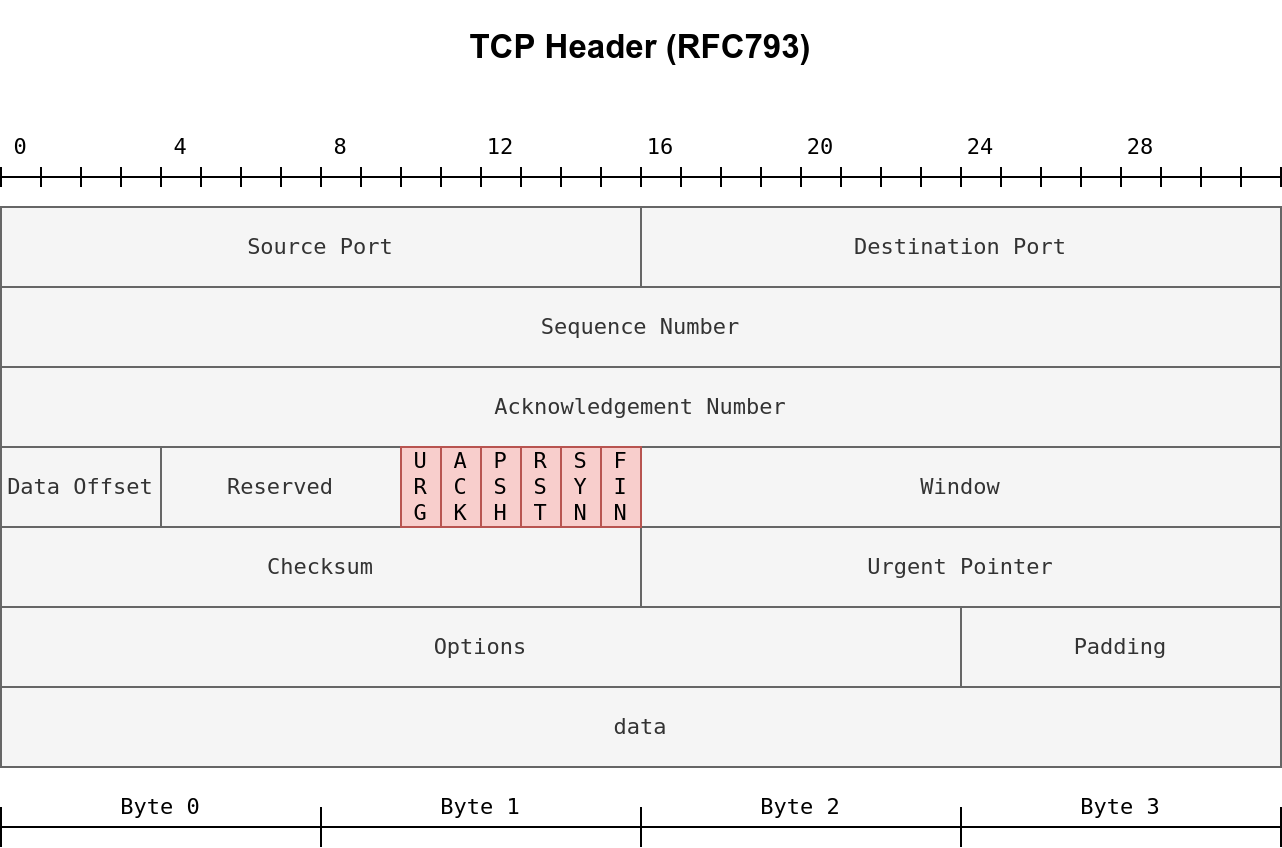
The pic above is a RFC 793 Header.
TCP flags are highlighted in red. Setting a flag bit means setting its value to 1. From left to right, the TCP header flags are:
1
2
3
4
5
6
1. URG: Urgent flag indicates that the urgent pointer filed is significant. The urgent pointer indicates that the incoming data is urgent, and that a TCP segment with the URG flag set is processed immediately without consideration of having to wait on previously sent TCP segments.
2. ACK: Acknowledgement flag indicates that the acknowledgement number is significant. It is used to acknowledge the receipt of a TCP segment.
3. PSH: Push flag asking TCP to pass the data to the application promptly.
4. RST: Reset flag is used to reset the connection. Another device, such as a firewall, might send it to tear a TCP connection. This flag is also used when data is sent to a host and there is no service on the receiving end to answer.
5. SYN: Synchronize flag is used to initiate a TCP 3-way handshake and synchronize sequence numbers with the other host. The sequence number should be set randomly during TCP connection establishment.
6. FIN: The sender has no more data to send.
Answer the questions below
What 3 letters represent the Reset flag? RST
Which flag needs to be set when you initiate a TCP connection (first packet of TCP 3-way handshake)? SYN
Task 4 - TCP Connect Scan
-sT (TCP Connect Scan)
Answer the questions below
Launch the VM. Open the AttackBox and execute nmap -sT 10.10.192.196 via the terminal. A new service has been installed on this VM since our last scan. Which port number was closed in the scan above but is now open on this target VM? 110
What is Nmap’s guess about the newly installed service? pop3
Task 5 - TCP SYN Scan
-sN (TCP SYN scan) required root or sudoer to use it. SYN scan does not need to complete the TCP 3-way handshake; instead, it tears down the connection once it receives a response from the server. Because we didn’t establish a TCP connection, this decreases the chances of the scan being logged.
Answer the questions below
Launch the VM. Some new server software has been installed since the last time we scanned it. On the AttackBox, use the terminal to execute nmap -sS 10.10.185.20. What is the new open port? 6667
What is Nmap’s guess of the service name? irc
Task 6 - UDP Scan
-sU UDP is a connectionless protocol, and hence it does not require any handshake for connection establishment. We cannot guarantee that a service listening on a UDP port would respond to our packets. However, if a UDP packet is sent to a closed port, an ICMP port unreachable error (type 3, code 3) is returned. It does require root or sudoer user.
Answer the questions below
Launch the VM. On the AttackBox, use the terminal to execute nmap -sU -F -v MACHINE_IP. A new service has been installed since the last scan. What is the UDP port that is now open? 53
What is the service name according to Nmap? domain
Task 7 - Fine-Tuning Scope and Performance
- port list:
-p22,80,443will scan ports 22, 80 and 443. - port range:
-p1-1023will scan all ports between 1 and 1023 inclusive, while-p20-25will scan ports between 20 and 25 inclusive.
You can request the scan of all ports by using -p-, which will scan all 65535 ports. If you want to scan the most common 100 ports, add -F. Using --top-ports 10 will check the ten most common ports.
You can control the scan timing using -T<0-5>. -T0 is the slowest (paranoid), while -T5 is the fastest.
Answer the questions below
What is the option to scan all the TCP ports between 5000 and 5500? -p5000-5500
How can you ensure that Nmap will run at least 64 probes in parallel? –min-parallelism=64
What option would you add to make Nmap very slow and paranoid? -T0
Task 8 - Summary
This room covered three types of scans.
| Port Scan Type | Example Command |
|---|---|
| TCP Connect Scan | nmap -sT 10.10.139.67 |
| TCP SYN Scan | sudo nmap -sS 10.10.139.67 |
| UDP Scan | sudo nmap -sU 10.10.139.67 |
These scan types should get you started discovering running TCP and UDP services on a target host.
| Option | Purpose |
|---|---|
| -p- | all ports |
| -p1-1023 | scan ports 1 to 1023 |
| -F | 100 most common ports |
| -r | scan ports in consecutive order |
| -T<0-5> | -T0 being the slowest and T5 the fastest |
| –max-rate 50 | rate <= 50 packets/sec |
| –min-rate 15 | rate >= 15 packets/sec |
| –min-parallelism 100 | at least 100 probes in parallel |