Basics of PowerShell and PowerShell Scripting
https://tryhackme.com/room/powershell
Task 1 - Objectives
In this room, we’ll be exploring the following concepts:
- What is Powershell and how it works
- Basic Powershell commands
- Windows enumeration with Powershell
- Powershell scripting
Task 2 - What is Powershell?
- Powesherll is the Windows Scripting Language, and shell enviroment.
- Powershell commands, called cmdlets, are written in .NET.
- the output of cmdlets are objects
- this means running cmdlets allows us to perform actions on the output object (passing output from one cmdlet to another)
- The normal format of a cmdlet is represented using Verb-Noun; example cmdlet to list commands is called Get-Command
Common Powershell Verbs
- Get
- Start
- Stop
- Read
- Write
- New
- Out
- Full List of Approved Verbs
Answer the questions below
What is the command to get help about a particular cmdlet(without any parameters)?
Get-Help
Task 3 - Basic Powershell Commands
Get-CommandandGet-Helpare our new best friends :smile:
Using Get-Command
Get-CommandGets all cmdlets installed on the computer - Example useageGet-Command Verb-*orGet-Command *-Noun- Running
Get-Command New-*will view all the cmdlets for the verb New.
Object Manipulation
- Since all outputs of every cmdlet is an object we can pass output to other cmdlets, and use specific object cmdlets to extract information
- We can do this with the Pipeline (
|) - After the pipe, powershell passes an object to the next cmdlet.
- An object contains methods and properties
- We can think of methods as functions that can be applied to output from the cmdlet, and think of peoperties as vartiable in the output from a cmdlet.
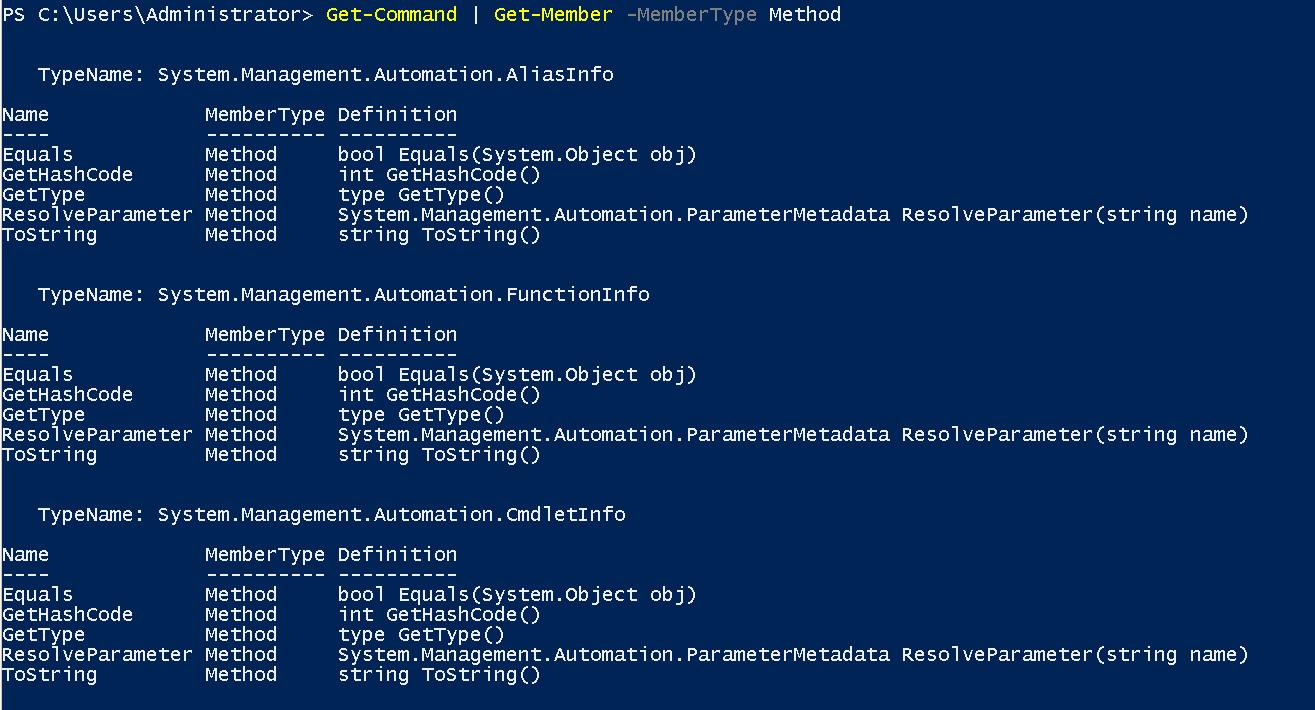
- To view these details pass the output of a cmdlet to the Get-Member cmdlet
Verb-Noun | Get-Memberexample of running this to view members for the Get-Command isGet-Command | Get-Member -MemberType Methodwe can select betweenMethodand-MemberType Properties
Creating Objects From Previous cmdlets
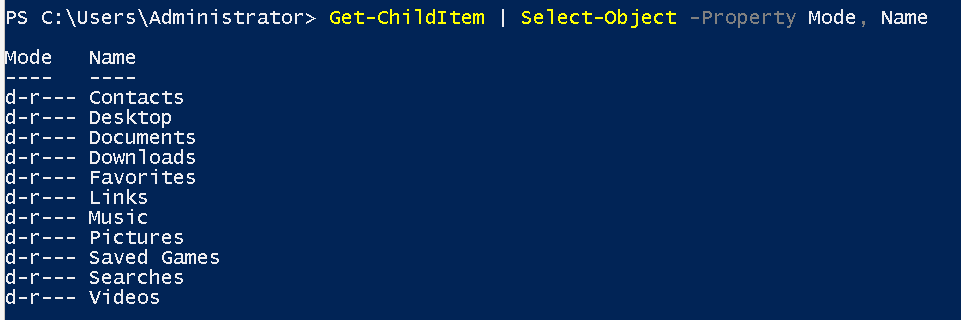
- We can manipulate objects by pulling out the peoperties from the output of a cmdlet and creating a new object with
Select-Object - Example of listing the Directories and selecting mode and name
We can also use these flags to select information:
- first - gets the first x object
- last - gets the last x object
- unique - shows the unique objects
- skip - skips x objects
Filtering Objects
- Wgeb retrieving output objects, we can select objects that match specific values. We can do this using
Where-Objectto filter based on the value of peoperties. - The general format of using this cmdlet:
Verb-Noun | Where-Object -Property PropertyName -operator ValueVerb-Noun | Where-Object {$_.PropertyName -operator Value}
The second version uses the $_ operator to iterate through every object passed to the Where-Object cmdlet.
Where -operator is a list of the following operators:
- Contains: if any item in the property value is an exact match for the specified value
- EQ: if the property value is the same as the specified value
- GT: if the property value is greater than the specified value
- Match: Actually works where EQ doesnt
Example for Get-Service where Services are running: Get-Service | Where-Object -Property Status -eq Running
Sort Object
- When cmdlet’s output a lot of info, we can sort it to extract the information more efficiently.
- We can do this bu pupe lining the output to the
Sort-Objectcmdlet - Example format:
Verb-Noun | Sort-Object
Now Lets try some commands out.
Answer the questions below
What is the location of the file “interesting-file.txt”
Get-ChildItem -Path C:\ -Recurse -Filter interesting-file.* -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Specify the contents of this file
Get-Content -Path 'C:\Program Files\interesting-file.txt.txt'
How many cmdlets are installed on the system(only cmdlets, not functions and aliases)?
Get-Command -CommandType Cmdlet | Measure-Object
Get the MD5 hash of interesting-file.txt
Get-FileHash .\interesting-file.txt.txt -Algorithm MD5
What is the command to get the current working directory?
Get-Location
Does the path “C:\Users\Administrator\Documents\Passwords” Exist(Y/N)?
Get-Content -Path 'C:\Users\Administrator\Documents\Passwords' -Force
What command would you use to make a request to a web server?
Invoke-WebRequest
Base64 decode the file b64.txt on Windows.
Get-Childitem -Path C:\ -Recurse -Filter b64.* -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
certutil -decode "C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\b64.txt" decode.txtGet-Content .\decode.txt
Task 4 - Enumeration
The first step when you have gained initial access to any machine would be to enumerate. We’ll be enumerating the following:
- users
- basic networking information
- file permissions
- registry permissions
- scheduled and running tasks
- insecure files
Answer the questions below
How many users are there on the machine?
Get-Localuser
Which local user does this SID(S-1-5-21-1394777289-3961777894-1791813945-501) belong to?
Get-LocalUser | select Name,SID
How many users have their password required values set to False?
Get-Localuser | Format-ListGet-LocalUser | Where-Object -Property PasswordRequired -Match False
How many local groups exist?
Get-LocalGroup | Measure-Object
What command did you use to get the IP address info?
Get-NetIPAddress
How many ports are listed as listening?
Get-NetTCPConnection | where -Property state -EQ listen | measure
What is the remote address of the local port listening on port 445?
Get-NetTCPConnection | where -Property LocalPort -EQ 445 | Format-List
How many patches have been applied?
Get-hotfix | measure
When was the patch with ID KB4023834 installed?
Get-Hotfix | where -Property HotFixID -EQ KB4023834 | Format-list
Find the contents of a backup file.
Get-ChildItem -Path C:\ -Recurse -Filter *.bak* -ErrorAction SilentlyContinueGet-Content "C:\Program Files (x86)\Internet Explorer\passwords.bak.txt"
Search for all files containing API_KEY
Get-ChildItem C:\* -Recurse | Select-String -pattern API_KEY
What command do you do to list all the running processes?
Get-Process
What is the path of the scheduled task called new-sched-task?
Get-ScheduledTask | where TaskName -eq new-sched-task | Format-List
Who is the owner of the C:
Get-Acl c:
Task 5 - Basic Scripting Challenge
Answer the questions below
What file contains the password?
1
2
3
4
$path = "C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\emails"
$string_pattern = "password"
$command = Get-ChildItem -Path $path -Recurse | Select-String -Pattern $string_pattern
echo $command
What is the password?
1
2
3
4
$path = "C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\emails"
$string_pattern = "password"
$command = Get-ChildItem -Path $path -Recurse | Select-String -Pattern $string_pattern
echo $command
What files contains an HTTPS link?
1
2
3
4
$path = "C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\emails"
$string_pattern = "https"
$command = Get-ChildItem -Path $path -Recurse | Select-String -Pattern $string_pattern
echo $command
Task 6 Intermediate Scripting
Now that you’ve learnt a little bit about how scripting works - let’s try something a bit more interesting. Sometimes we may not have utilities like nmap and python available, and we are forced to write scripts to do very rudimentary tasks. Why don’t you try writing a simple port scanner using Powershell. Here’s the general approach to use:
- Determine IP ranges to scan(in this case it will be localhost) and you can provide the input in any way you want
- Determine the port ranges to scan
- Determine the type of scan to run(in this case it will be a simple TCP Connect Scan)
Answer the questions below
How many open ports did you find between 130 and 140(inclusive of those two)?
1
2
3
4
5
6
$portlow = 130
$porthigh = 140
for($i=$portlow; $i -le $porthigh; $i++){
Test-NetConnection localhost -Port $i | Where TcpTestSucceeded -EQ True
}