Learn about digital forensics and related processes and experiment with a practical example.
Security/Digital Forensics/Forensics/Metadata
Introduction To Digital Forensics
Forensics is the application of science to investigate crimes and establish facts. With the use and spread of digital systems, such as computers and smartphones, a new branch of forensics was born to investigate related crimes: computer forensics, which later evolved into, digital forensics.
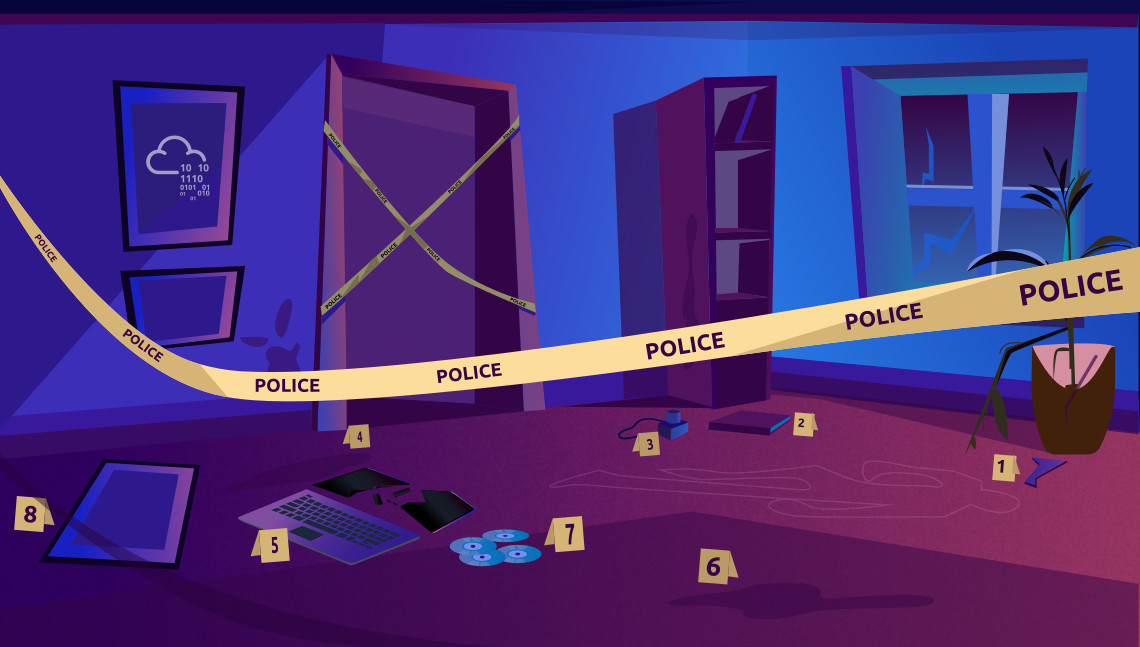
Think about the following scenario. The law enforcement agents arrive at a crime scene; however, part of this crime scene includes digital devices and media. Digital devices include desktop computers, laptops, digital cameras, music players, and smartphones, to name a few. Digital media includes CDs, DVDs, USB flash memory drives, and external storage. A few questions arise:
- How should the police collect digital evidence, such as smartphones and laptops? What are the procedures to follow if the computer and smartphone are running?
- How to transfer the digital evidence? Are there certain best practices to follow when moving computers, for instance?
- How to analyze the collected digital evidence? Personal device storage ranges between tens of gigabytes to several terabytes; how can this be analyzed.
Assuming this employee is suspected in the figure above, we can quickly see the digital devices that might be of interest to an investigation. We notice a tablet, a smartphone, a digital camera, and a USB flash memory in addition to a desktop computer. Any of these devices might contain a trove of information that can help with an investigation. Processing these as evidence would require digital forensics.
More formally, digital forensics is the application of computer science to investigate digital evidence for a legal purpose. Digital forensics is used in two types of investigations:
- Public-sector investigations refer to the investigations carried out by government and law enforcement agencies. They would be part of a crime or civil investigation.
- Private-sector investigations refer to the investigations carried out by corporate bodies by assigning a private investigator, whether in-house or outsourced. They are triggered by corporate policy violations.
Whether investigating a crime or a corporate policy violation, part of the evidence is related to digital devices and digital media. This is where digital forensics comes into play and tries to establish what has happened. Without trained digital forensics investigators, it won’t be possible to process any digital evidence properly.
Digital Forensics Process
As a digital forensics investigator, you arrive at a scene similar to the one shown in the image above. What should you do as a digital forensics investigator? After getting the proper legal authorization, the basic plan goes as follows:
- Acquire the evidence: Collect the digital devices such as laptops, storage devices, and digital cameras. (Note that laptops and computers require special handling if they are turned on; however, this is outside the scope of this room.)
- Establish a chain of custody: Fill out the related form appropriately (Sample form). The purpose is to ensure that only the authorized investigators had access to the evidence and no one could have tampered with it.
- Place the evidence in a secure container: You want to ensure that the evidence does not get damaged. In the case of smartphones, you want to ensure that they cannot access the network, so they don’t get wiped remotely.
- Transport the evidence to your digital forensics lab.
At the lab, the process goes as follows:
- Retrieve the digital evidence from the secure container.
- Create a forensic copy of the evidence: The forensic copy requires advanced software to avoid modifying the original data.
- Return the digital evidence to the secure container: You will be working on the copy. If you damage the copy, you can always create a new one.
- Start processing the copy on your forensics workstation.
The above steps have been adapted from Guide to Computer Forensics and Investigations, 6th Edition.
More generally, according to the former director of the Defense Computer Forensics Laboratory, Ken Zatyko, digital forensics includes:
- Proper search authority: Investigators cannot commence without the proper legal authority. Chain of custody: This is necessary to keep track of who was holding the evidence at any time.
- Validation with mathematics: Using a special kind of mathematical function, called a hash function, we can confirm that a file has not been modified.
- Use of validated tools: The tools used in digital forensics should be validated to ensure that they work correctly. For example, if you are creating an image of a disk, you want to ensure that the forensic image is identical to the data on the disk.
- Repeatability: The findings of digital forensics can be reproduced as long as the proper skills and tools are available.
- Reporting: The digital forensics investigation is concluded with a report that shows the evidence related to the case that was discovered.
Practical Example of Digital Forensics
Everything we do on our digital devices, from smartphones to computers, leaves traces. Let’s see how we can use this in the subsequent investigation.
Our cat, Gado, has been kidnapped. The kidnapper has sent us a document with their requests in MS Word Document format. We have converted the document to PDF format and extracted the image from the MS Word file for your convenience.
You can download the attached file to your local machine for inspection; however, for your convenience we have added the files to the AttackBox. To follow along, open the terminal on the AttackBox, then go to the directory /root/Rooms/introdigitalforensics as shown below. In the following terminal output, we changed to the directory containing the case files.
1
2
3
4
root# cd /root/Rooms
root# cd introdigitalforensics
root# ls
letter-image.jpg ransom-letter.doc ransom-letter.pdf ransom-lettter-2.zip
Document Metadata
When you create a text file, TXT, some metadata gets saved by the Operating System, such as file creation date and last modification date. However, much information gets kept within the file’s metadata when you use a more advanced editor, such as MS Word. There are various ways to read the file metadata; you might open them within their official viewer/editor or use a suitable forensic tool. Note that exporting the file to other formats, such as PDF, would maintain most of the metadata of the original document, depending on the PDF writer used.
Let’s see what we can learn from the PDF file. We can try to read the metadata using the program pdfinfo. Pdfinfo displays various metadata related to a PDF file, such as title, subject, author, creator, and creation date. (The AttackBox already has pdfinfo installed; however, if you are using Kali Linux and don’t have pdfinfo installed, you can install it using sudo apt install poppler-utils.) Consider the following example of using pdfinfo DOCUMENT.pdf.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
user@TryHackMe$ pdfinfo DOCUMENT.pdf
Creator: Microsoft® Word for Office 365
Producer: Microsoft® Word for Office 365
CreationDate: Wed Oct 10 21:47:53 2018 EEST
ModDate: Wed Oct 10 21:47:53 2018 EEST
Tagged: yes
UserProperties: no
Suspects: no
Form: none
JavaScript: no
Pages: 20
Encrypted: no
Page size: 595.32 x 841.92 pts (A4)
Page rot: 0
File size: 560362 bytes
Optimized: no
PDF version: 1.7
The PDF metadata clearly shows that it was created using MS Word for Office 365 on October 10, 2018.
Answer the questions below
Using pdfinfo, find out the author of the attached PDF file.
pdfinfo ransom-letter.pdf- Ann Gree Shepherd
Photo EXIF Data
EXIF stands for Exchangeable Image File Format; it is a standard for saving metadata to image files. Whenever you take a photo with your smartphone or with your digital camera, plenty of information gets embedded in the image. The following are examples of metadata that can be found in the original digital images:
- Camera model / Smartphone model
- Date and time of image capture
- Photo settings such as focal length, aperture, shutter speed, and ISO settings
Because smartphones are equipped with a GPS sensor, finding GPS coordinates embedded in the image is highly probable. The GPS coordinates, i.e., latitude and longitude, would generally show the place where the photo was taken.
There are many online and offline tools to read the EXIF data from images. One command-line tool is exiftool. ExifTool is used to read and write metadata in various file types, such as JPEG images. (The AttackBox already has exiftool installed; however, if you are using Kali Linux and don’t have exiftool installed, you can install it using sudo apt install libimage-exiftool-perl.) In the following terminal window, we executed exiftool IMAGE.jpg to read all the EXIF data embedded in this image. Terminal
1
2
3
4
user@TryHackMe$ exiftool IMAGE.jpg
[...]
GPS Position : 51 deg 31' 4.00" N, 0 deg 5' 48.30" W
[...]
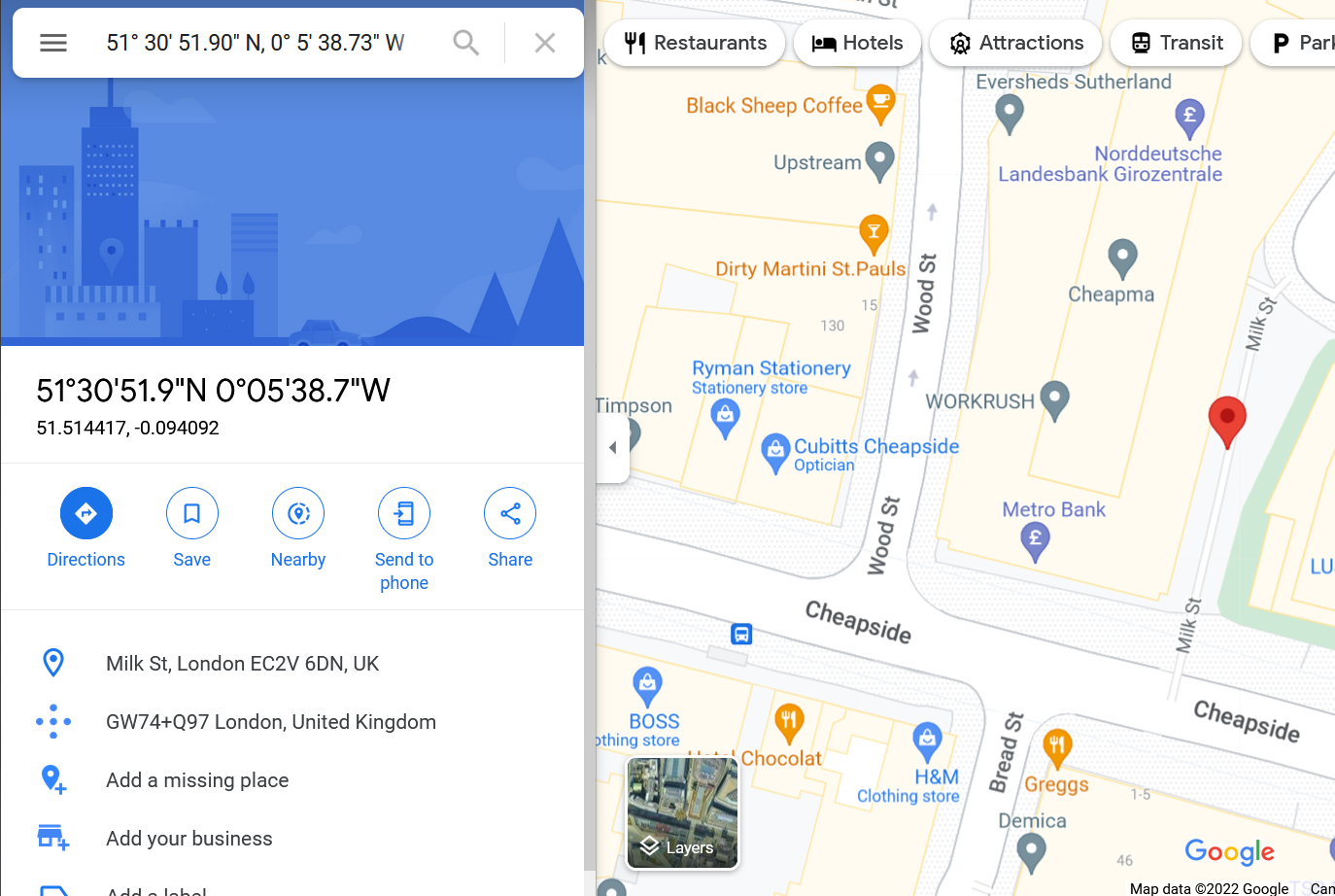
If you take the above coordinates and search one of the online maps, you will learn more about this location. Searching Microsoft Bing Maps or Google Maps for 51° 31’ 4.00” N, 0° 5’ 48.30” W reveals that these coordinates indicate that the image was taken very near to the Museum of London. (We only replaced deg with ° for our search to work.) We noticed that the coordinates were converted to decimal representation on the search page: 51.517776, -0.09675.
Using exiftool or any similar tool, try to find where the kidnappers took the image they attached to their document. What is the name of the street?
What is the model name of the camera used to take this photo?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
ExifTool Version Number : 12.42
File Name : letter-image.jpg
Directory : .
File Size : 127 kB
File Modification Date/Time : 2022:02:23 00:53:33-08:00
File Access Date/Time : 2022:07:12 10:20:12-07:00
File Inode Change Date/Time : 2022:07:10 22:34:27-07:00
File Permissions : -rwxr-xr-x
File Type : JPEG
File Type Extension : jpg
MIME Type : image/jpeg
JFIF Version : 1.01
Exif Byte Order : Little-endian (Intel, II)
Compression : JPEG (old-style)
Make : Canon
Camera Model Name : Canon EOS R6
Orientation : Horizontal (normal)
X Resolution : 300
Y Resolution : 300
Resolution Unit : inches
Software : GIMP 2.10.28
Modify Date : 2022:02:15 17:23:40
Exposure Time : 1/200
F Number : 2.8
Exposure Program : Manual
ISO : 640
Sensitivity Type : Recommended Exposure Index
Recommended Exposure Index : 640
Exif Version : 0231
Date/Time Original : 2022:02:25 13:37:33
Create Date : 2022:02:25 13:37:33
Offset Time : +01:00
Offset Time Original : +03:00
Offset Time Digitized : +03:00
Shutter Speed Value : 1/200
Aperture Value : 2.8
Exposure Compensation : 0
Max Aperture Value : 1.8
Metering Mode : Multi-segment
Flash : No Flash
Focal Length : 50.0 mm
User Comment : THM{238956}
Sub Sec Time Original : 42
Sub Sec Time Digitized : 42
Color Space : sRGB
Exif Image Width : 7900
Exif Image Height : 5267
Focal Plane X Resolution : 1520
Focal Plane Y Resolution : 1520
Focal Plane Resolution Unit : cm
Custom Rendered : Normal
Exposure Mode : Manual
White Balance : Auto
Scene Capture Type : Standard
Serial Number : 083021002010
Lens Info : 50mm f/?
Lens Model : EF50mm f/1.8 STM
Lens Serial Number : 000029720b
GPS Latitude Ref : North
GPS Longitude Ref : West
GPS Time Stamp : 13:37:33
Subfile Type : Reduced-resolution image
Photometric Interpretation : YCbCr
Samples Per Pixel : 3
Thumbnail Offset : 1214
Thumbnail Length : 4941
XMP Toolkit : XMP Core 4.4.0-Exiv2
Api : 2.0
Platform : Linux
Time Stamp : 1644938627130718
Approximate Focus Distance : 0.79
Distortion Correction Already Applied: True
Firmware : 1.2.0
Flash Compensation : 0
Image Number : 0
Lateral Chromatic Aberration Correction Already Applied: True
Lens : EF50mm f/1.8 STM
Vignette Correction Already Applied: True
Color Mode : RGB
ICC Profile Name : Adobe RGB (1998)
Creator Tool : GIMP 2.10
Metadata Date : 2021:12:02 13:32:48+01:00
Rating : 2
Document ID : adobe:docid:photoshop:de96cdf3-afbf-664d-9d4c-d5c1d0fdb4e1
Instance ID : xmp.iid:b80f5656-424a-4d4d-9cd0-5a36706d26d6
Original Document ID : D3825C53382EED70DB7435B0CCF756F5
Preserved File Name : 5L0A2971.CR3
Already Applied : True
Auto Lateral CA : 1
Blacks 2012 : 0
Blue Hue : 0
Blue Saturation : 0
Camera Profile : Adobe Standard
Camera Profile Digest : 441F68BD6BC3369B59256B103CE2CD5C
Clarity 2012 : 0
Color Grade Blending : 50
Color Grade Global Hue : 0
Color Grade Global Lum : 0
Color Grade Global Sat : 0
Color Grade Highlight Lum : 0
Color Grade Midtone Hue : 0
Color Grade Midtone Lum : 0
Color Grade Midtone Sat : 0
Color Grade Shadow Lum : 0
Color Noise Reduction : 25
Color Noise Reduction Detail : 50
Color Noise Reduction Smoothness: 50
Contrast 2012 : 0
Crop Angle : 0
Crop Bottom : 1
Crop Constrain To Warp : 0
Crop Left : 0
Crop Right : 1
Crop Top : 0
Defringe Green Amount : 0
Defringe Green Hue Hi : 60
Defringe Green Hue Lo : 40
Defringe Purple Amount : 0
Defringe Purple Hue Hi : 70
Defringe Purple Hue Lo : 30
Dehaze : 0
Exposure 2012 : -0.40
Grain Amount : 0
Green Hue : 0
Green Saturation : 0
Has Crop : False
Has Settings : True
Highlights 2012 : -32
Hue Adjustment Aqua : 0
Hue Adjustment Blue : 0
Hue Adjustment Green : 0
Hue Adjustment Magenta : 0
Hue Adjustment Orange : 0
Hue Adjustment Purple : 0
Hue Adjustment Red : 0
Hue Adjustment Yellow : 0
Lens Manual Distortion Amount : 0
Lens Profile Digest : B23331240701D3B28825B46A4802290C
Lens Profile Distortion Scale : 100
Lens Profile Enable : 1
Lens Profile Filename : Canon EOS-1Ds Mark III (Canon EF 50mm f1.8 STM) - RAW.lcp
Lens Profile Is Embedded : False
Lens Profile Name : Adobe (Canon EF 50mm f/1.8 STM)
Lens Profile Setup : LensDefaults
Lens Profile Vignetting Scale : 100
Luminance Adjustment Aqua : 0
Luminance Adjustment Blue : 0
Luminance Adjustment Green : 0
Luminance Adjustment Magenta : 0
Luminance Adjustment Orange : 0
Luminance Adjustment Purple : 0
Luminance Adjustment Red : 0
Luminance Adjustment Yellow : 0
Luminance Smoothing : 0
Override Look Vignette : False
Parametric Darks : 0
Parametric Highlight Split : 75
Parametric Highlights : 0
Parametric Lights : 0
Parametric Midtone Split : 50
Parametric Shadow Split : 25
Parametric Shadows : 0
Perspective Aspect : 0
Perspective Horizontal : 0
Perspective Rotate : 0.0
Perspective Scale : 100
Perspective Upright : 0
Perspective Vertical : 0
Perspective X : 0.00
Perspective Y : 0.00
Post Crop Vignette Amount : 0
Process Version : 11.0
Raw File Name : 5L0A2971.dng
Red Hue : 0
Red Saturation : 0
Saturation : 0
Saturation Adjustment Aqua : 0
Saturation Adjustment Blue : 0
Saturation Adjustment Green : 0
Saturation Adjustment Magenta : 0
Saturation Adjustment Orange : 0
Saturation Adjustment Purple : 0
Saturation Adjustment Red : 0
Saturation Adjustment Yellow : 0
Shadow Tint : 0
Shadows 2012 : 0
Sharpen Detail : 25
Sharpen Edge Masking : 60
Sharpen Radius : +1.0
Sharpness : 45
Split Toning Balance : 0
Split Toning Highlight Hue : 0
Split Toning Highlight Saturation: 0
Split Toning Shadow Hue : 0
Split Toning Shadow Saturation : 0
Color Temperature : 6650
Texture : 0
Tint : -7
Tone Curve Name 2012 : Linear
Tone Curve PV2012 : 0, 0, 255, 255
Tone Curve PV2012 Blue : 0, 0, 255, 255
Tone Curve PV2012 Green : 0, 0, 255, 255
Tone Curve PV2012 Red : 0, 0, 255, 255
Version : 14.0.1
Vibrance : 0
Vignette Amount : 0
Whites 2012 : 0
Format : image/jpeg
Document Ancestors : xmp.did:2ec1b1a6-ffae-0a44-90f9-3b6998456cdf, xmp.did:780a63d9-6024-e942-baf4-cae80b62a8c5
Derived From Document ID : xmp.did:c3f1ef49-6aa6-4441-8800-6afa19131d22
Derived From Instance ID : xmp.iid:fd37b6b6-4a37-d44a-89e0-3710c289a8db
Derived From Original Document ID: D3825C53382EED70DB7435B0CCF756F5
History Action : derived, saved, saved, saved, derived, saved, converted, saved, saved, converted, derived, saved, saved
History Parameters : converted from image/x-canon-cr3 to image/dng, saved to new location, converted from image/dng to image/vnd.adobe.photoshop, saved to new location, from image/vnd.adobe.photoshop to application/vnd.adobe.photoshop, from application/vnd.adobe.photoshop to image/jpeg, converted from application/vnd.adobe.photoshop to image/jpeg
History Changed : /, /metadata, /metadata, /, /, /, /, /
History Instance ID : xmp.iid:68afaab8-00f8-4a17-880d-04362acf7f59, xmp.iid:a415f140-19e3-dd4f-a523-2a91fd837241, xmp.iid:a732c1b4-c918-d649-91df-a08fd30a3b28, xmp.iid:c3f1ef49-6aa6-4441-8800-6afa19131d22, xmp.iid:e03136da-36b8-4a4f-a00f-4e953a46cb21, xmp.iid:fd37b6b6-4a37-d44a-89e0-3710c289a8db, xmp.iid:b0dfac61-4499-6b47-b061-c79f9c8868d9, xmp.iid:defc8f04-ab7b-4648-b9d4-1da9f1aa9bf9
History Software Agent : Adobe Photoshop Lightroom Classic 10.2 (Macintosh), Adobe Photoshop Camera Raw 14.0, Adobe Photoshop Camera Raw 14.0.1 (Windows), Adobe Photoshop Camera Raw 14.0.1 (Windows), Adobe Photoshop 22.4 (Windows), Adobe Photoshop 22.4 (Windows), Adobe Photoshop 22.4 (Windows), Gimp 2.10 (Linux)
History When : 2021:11:15 15:50:41+03:00, 2021:12:01 11:25:22+01:00, 2021:12:01 12:34:12+01:00, 2021:12:02 10:19:47+01:00, 2021:12:02 12:53:12+01:00, 2021:12:02 13:32:48+01:00, 2021:12:02 13:32:48+01:00, 2022:02:15 17:23:47+02:00
Look Amount : 1
Look Copyright : © 2018 Adobe Systems, Inc.
Look Group : lang="x-default" Profiles
Look Name : Adobe Color
Look Supports Amount : false
Look Supports Monochrome : false
Look Supports Output Referred : false
Look UUID : B952C231111CD8E0ECCF14B86BAA7077
Look Parameters Camera Profile : Adobe Standard
Look Parameters Convert To Grayscale: False
Look Parameters Look Table : E1095149FDB39D7A057BAB208837E2E1
Look Parameters Process Version : 11.0
Look Parameters Tone Curve PV2012: 0, 0, 22, 16, 40, 35, 127, 127, 224, 230, 240, 246, 255, 255
Look Parameters Tone Curve PV2012 Blue: 0, 0, 255, 255
Look Parameters Tone Curve PV2012 Green: 0, 0, 255, 255
Look Parameters Tone Curve PV2012 Red: 0, 0, 255, 255
Look Parameters Version : 14.0.1
Profile CMM Type : Little CMS
Profile Version : 4.3.0
Profile Class : Display Device Profile
Color Space Data : RGB
Profile Connection Space : XYZ
Profile Date Time : 2022:02:15 14:53:19
Profile File Signature : acsp
Primary Platform : Apple Computer Inc.
CMM Flags : Not Embedded, Independent
Device Manufacturer :
Device Model :
Device Attributes : Reflective, Glossy, Positive, Color
Rendering Intent : Perceptual
Connection Space Illuminant : 0.9642 1 0.82491
Profile Creator : Little CMS
Profile ID : 0
Profile Description : GIMP built-in sRGB
Profile Copyright : Public Domain
Media White Point : 0.9642 1 0.82491
Chromatic Adaptation : 1.04788 0.02292 -0.05022 0.02959 0.99048 -0.01707 -0.00925 0.01508 0.75168
Red Matrix Column : 0.43604 0.22249 0.01392
Blue Matrix Column : 0.14305 0.06061 0.71393
Green Matrix Column : 0.38512 0.7169 0.09706
Red Tone Reproduction Curve : (Binary data 32 bytes, use -b option to extract)
Green Tone Reproduction Curve : (Binary data 32 bytes, use -b option to extract)
Blue Tone Reproduction Curve : (Binary data 32 bytes, use -b option to extract)
Chromaticity Channels : 3
Chromaticity Colorant : Unknown (0)
Chromaticity Channel 1 : 0.64 0.33002
Chromaticity Channel 2 : 0.3 0.60001
Chromaticity Channel 3 : 0.15001 0.06
Device Mfg Desc : GIMP
Device Model Desc : sRGB
Current IPTC Digest : b417d6571f8aba97a1e64afbdedafbdb
Coded Character Set : UTF8
Envelope Record Version : 4
Date Created : 2022:02:15
Digital Creation Date : 2021:11:05
Digital Creation Time : 14:06:13+03:00
Application Record Version : 4
Time Created : 17:23:40-17:23
Image Width : 1200
Image Height : 800
Encoding Process : Progressive DCT, Huffman coding
Bits Per Sample : 8
Color Components : 3
Y Cb Cr Sub Sampling : YCbCr4:4:4 (1 1)
Aperture : 2.8
Image Size : 1200x800
Megapixels : 0.960
Scale Factor To 35 mm Equivalent: 0.7
Shutter Speed : 1/200
Create Date : 2022:02:25 13:37:33.42+03:00
Date/Time Original : 2022:02:25 13:37:33.42+03:00
Modify Date : 2022:02:15 17:23:40+01:00
Thumbnail Image : (Binary data 4941 bytes, use -b option to extract)
GPS Latitude : 51 deg 30' 51.90" N
GPS Longitude : 0 deg 5' 38.73" W
Date/Time Created : 2022:02:15 17:23:40-17:23
Digital Creation Date/Time : 2021:11:05 14:06:13+03:00
Circle Of Confusion : 0.043 mm
Depth Of Field : 0.06 m (0.76 - 0.82 m)
Field Of View : 54.9 deg
Focal Length : 50.0 mm (35 mm equivalent: 34.6 mm)
GPS Position : 51 deg 30' 51.90" N, 0 deg 5' 38.73" W
Hyperfocal Distance : 20.58 m
Light Value : 7.9
Lens ID : Canon EF 50mm f/1.8 STM